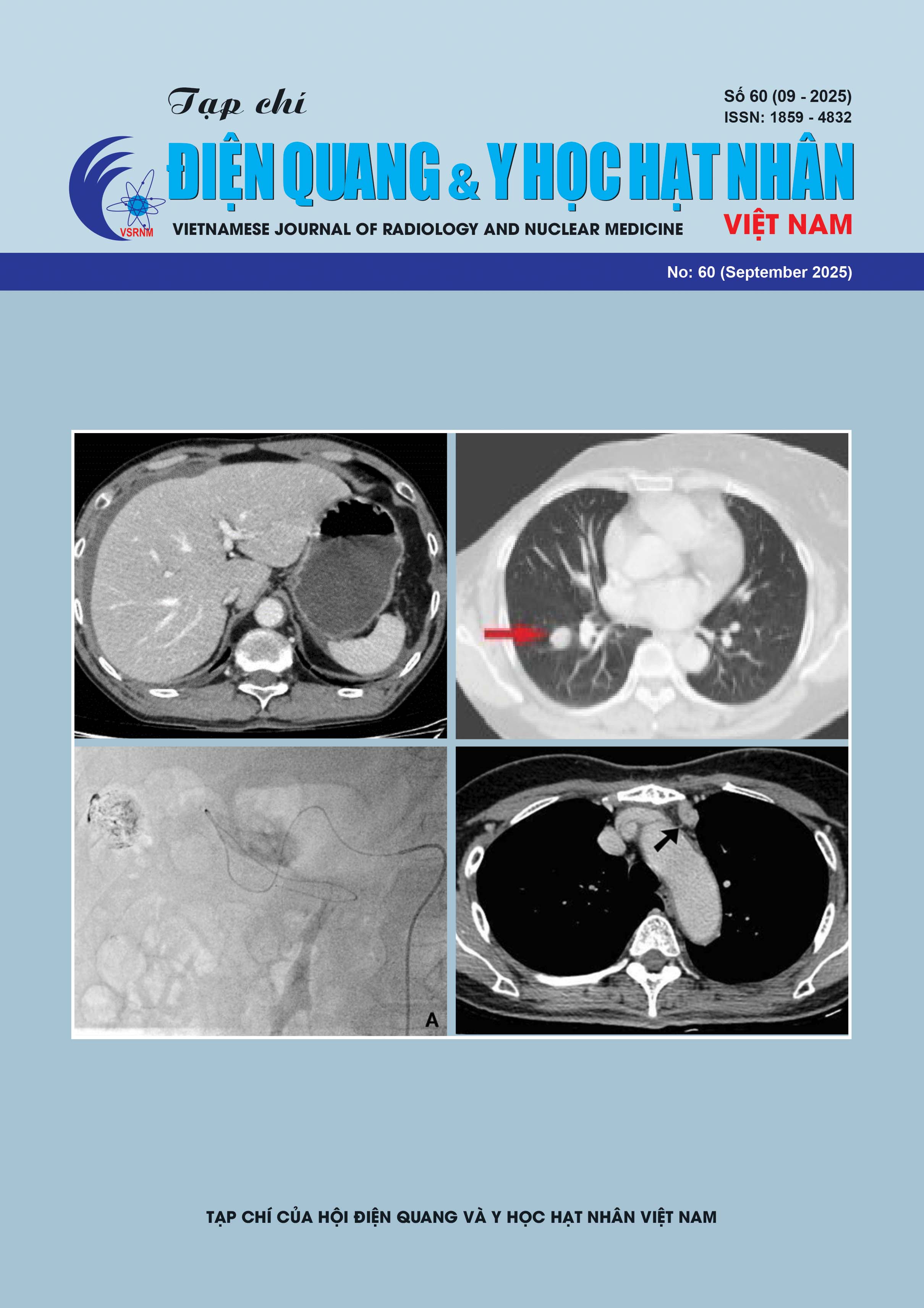
Imaging Characteristics of Pulmonary Metastases on Computed Tomography and Outcomes of Radiofrequency Ablation for Local Treatment of Pulmonary Metastases Under Robot Maxio Guidance
Abstract
Objective: To characterize the imaging features of pulmonary metastases on computed tomography (CT) and to evaluate the outcomes of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) for local treatment of pulmonary
metastases using Maxio robot guidance.
Methods: The study was a combined prospective and retrospective descriptive analysis conducted on 60 patients with pulmonary metastatic lesions, of whom 30 underwent radiofrequency ablation (RFA) under the guidance of the Maxio robotic system at the 108 Military Central Hospital between June 2021 and June 2025
Results: Most patients presented with multiple metastatic nodules rather than solitary ones. The most common sites were the right upper lobe and the lower lobes of both lungs. The mean tumor diameter was 25 ± 4.5 mm. The majority of lesions were solid nodules (86.7%). Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) was performed once in 19 patients, twice in 7 patients, and three times in 4 patients. The disease control rate reached 86.7%, with tumor necrosis observed at 6 months. One case of life-threatening massive hemoptysis was recorded.
Conclusion: Pulmonary metastatic lesions typically present as multiple, solid nodules, commonly located in the lower lobes of both lungs and the right upper lobe. Radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary
metastases under Maxio robotic guidance demonstrated favorable initial efficacy with a low complication rate.